Ebola virus
The World Health Organization (WHO) has alerted six African countries to watch out for potential cases of Ebola after it emerged in the Democratic Republic of Congo and Guinea.
The DRC declared the emergence of Ebola on February 7 while Guinea declared the outbreak on Sunday.
"We have already alerted the six countries around, including of course Sierra Leone and Liberia, and they are moving very fast to prepare and be ready and to look for any potential infection," the WHO's Margaret Harris told a Geneva briefing.
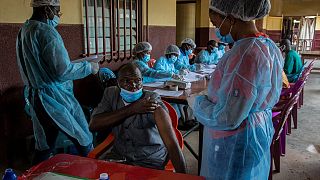
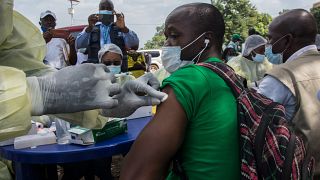
Meanwhile, the Ebola vaccination campaign kicked out Monday in areas where the epidemic was first reported.
Between 2013 and 2016 more than 11,000 people died in the West Africa Ebola epidemic, which began in Guinea.
Ebola infects humans through close contact with infected animals, such as chimpanzees and fruit bats. It then spreads between humans by direct contact with infected blood, fluids, and organs.
It can also be spread indirectly through contact with contaminated environments.











Go to video
DRC: Kabila arrives in rebel-held Goma after return from exile
01:53
Returning home to nothing: Displaced families in eastern DRC face dire humanitarian crisis
01:02
Former Guinean junta leader Moussa Dadis Camara leaves country for medical reasons
Go to video
U.S. charges Americans convicted of coup attempt in Congo
01:12
Cholera outbreak intensifies amidst violence in the DRC
Go to video
DRC: UN report highlights human rights violations linked to M23 group's offensive